Audi Engine Codes
At present, the designation of the Audi A6 engines and their volumes are not indicated in the vehicle’s passport. Only horsepower and kilowatts. This circumstance complicates the selection of auto parts, as it is necessary to decode the VIN code of the car, and for cars up to the 98th year of release this can not be done. How do I find out the car’s engine code ?? The table in this article allows us to quickly determine the engine code Audi A6 and volume by horsepower. All engines are listed as of mid-2014. Note that the Audi A6 engine code consists of a set of letters and numbers not exceeding 4 characters
Engines Audi – the directory
1.6 8V
This motor can be found under the hood of the Audi A3 (1st and 2nd generation) and A4 (B5 and B6). It was also widely used in other VW Group vehicles. In moderation decently, only the first A3, which weighs just over a ton, rides. A4 B6 for 1.6 is too heavy. The disadvantages include fuel consumption. 9 liters per 100 km seem disproportionately large for mediocre dynamics.
Pluses:
– simple construction;
– cheap repair;
– well tolerates the introduction of HBO;
– Low car cost.
Disadvantages:
– bad dynamics (overtaking is difficult, especially in the case of A4);
– a relatively high fuel consumption.

1.8 Turbo
The unit has a cast-iron block, a forged steel crankshaft and an aluminum block head with 20 valves (3 inlet and 2 exhaust per cylinder). To drive one camshaft, a toothed belt is used, and the second shaft is connected to the first short chain. KKK turbine without moving blades (unchanged geometry), and fuel injection – distributed. The unit in the “dry state” weighs about 150 kg.
Pluses:
– a good compromise between performance and fuel consumption;
– availability and availability of spare parts;
– a wide choice in the market.
Disadvantages:
– Several unpleasant typical defects in older cars with high mileage (oil consumption and timing faults).
Examples of application:
– Audi A3 I (8L);
– Audi TT I (8N);
– Audi A4 B5, B6 and B7.

2.4 V6
Despite the emergence of an increasingly strong turbo-turbo four-seater, Audi’s fans still prefer atmospheric petrol V6, especially in earlier versions. Of course, do not count on low fuel consumption – at least 10 liters per 100 km. The city will have to reckon with even 20 liters. But, the trip will seem pleasant.
Pluses:
– good elasticity;
– high reliability (only before updating);
– versions with distributed injection easily transfer the HBO installation.
Disadvantages:
– the limited sense of installing HBO in the updated version of FSI;
– expensive failures in the operation of the timing (FSI);
– a rather high fuel consumption.
Examples of application:
– Audi A4 II (B6);
– Audi A6 C5 and C6.

1.9 TDI
This is the most recognizable diesel of recent years. Even an elderly Audi with a 1.9 TDI is worth paying attention to – sturdy construction and inexpensive repairs.
1.9 TDI is the engine of the legend. It was produced in 1991 and has been modernized many times. It has found application in many other cars of VW Group.
The most reliable and cheap in operation and repair is the 90-strong version with injection pump of distribution type. The engine has a simple design, a constant geometry turbine and a single-mass flywheel.
Pluses:
– simple construction;
– good endurance;
– Low fuel consumption.
Disadvantages:
– many worn-out copies (the engine was installed until 2009, and since 2004 it was gradually replaced by a 2-liter turbodiesel);
– Low labor culture: noise and vibration, especially after starting a cold engine.
Examples of application:
– Audi A3 I (8L) and II (8P);
– Audi A4 B6 and B7;
– Audi A6 C4 and C5.
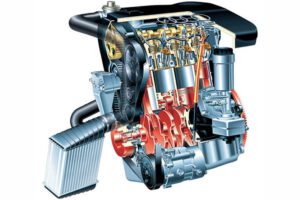
2.0 TDI CR
Buying Audi with the engine 2.0 TDI, you should check the history of the car. Often, these were cheap and economical versions, purchased for commercial or corporate garages. They have huge runs and are not always well served.
Pluses:
– good performance at an acceptable fuel consumption;
– good durability (especially in comparison with 2.0 TDI PD);
– a large variety of versions.
Disadvantages:
– expensive maintenance (complex construction and expensive spare parts);
– significant mileage of many specimens, despite a relatively young age.
Examples of application:
– Audi A4 III (B8);
– Audi Q5 (8R);
– Audi A6 III (C6).

3.0 TDI
The 3-liter turbodiesel was designed to correct the bad reputation of the Audi V6 diesel, spoiled by the 2.5 TDI V6. 3.0 TDI has earned respect not only thanks to its performance, but also its durability. Very strong were the unit, the cylinder head and the crank mechanism. For each cylinder there are 4 valves and one piezoelectric nozzle.
Pluses:
– high culture of work;
good performance;
– low fuel consumption;
– a good service life of many engine parts.
Disadvantages:
– Expensive in troubleshooting the timing, intake manifold and DPF;
– Many copies on the market have high mileage and dubious technical condition.
Examples of application:
– Audi A5 I (8T / 8F);
– Audi Q7 I (4L);
– Audi A8 II (D3).

Audi Engine Codes list pdf
audi-engine-codes